Shop
Shop
Showing 13–24 of 62 results
-
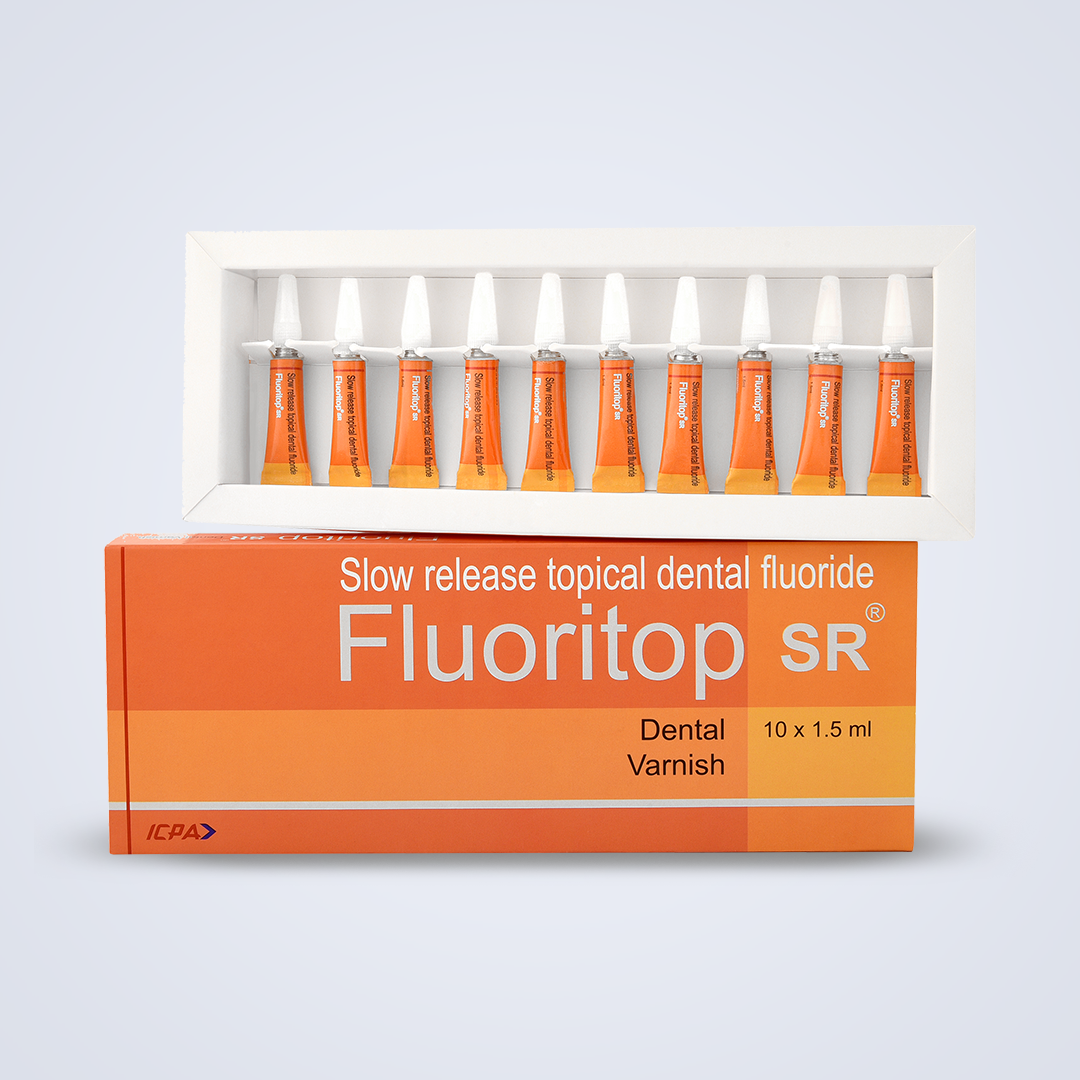
Fluoritop SR Varnish 10&#..
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Each ml contains
Sodium Fluoride I.P. 50mg Equivalent to 22.6mg of fluoride in slow release form 22,600 ppm of fluoride.
Alcohol-based varnish q.s.Mechanism Of Action:
Strengthens the enamel/ increased resistance to wear.
Increases resistance to acid attacks/prevents tooth decay.
Blocks open & sensitive dentinal tubules/ treats & prevents dentinal hypersensitivity.For Caries Prevention:
Dose: 0.3ml to 0.5ml (2 to 5 drops) for primary dentition 1ml (8 to 10 drops) for mix dentition 1ml to 1.5ml (10-15 drops) for adult dentition Frequency Of Application: Once in six months, for caries preventive action. For aggressive carious conditions once every 3 months.
For Hypersensitivity:
Dose: 0.5ml (4 to 5 drops) per quadrant.
Frequency Of Application: Once every week for three weeks or two applications in a week.Mode of Application:
Select teeth – Remove visible debris & deposits on the teeth surface.
Dry with an air syringe or cotton pledget.
Paint the recommended quantity of varnish on the tooth surface directly through the nozzle or with an applicator brush, cotton bud, probe, or cotton wool pledget.
Now, allow it to dry. After the varnish is painted on the tooth surface, it is reported to remain there for 12/15 hours. During this time, fluoride is deposited in the enamel.Precautions:
The patient should not eat or brush for at least 4 hours after varnish application.
Other fluoride preparations like gels and rinses should not be used for atleast 24 hrs after the varnish application.
Fluoride tablets are to be discontinued for several days after varnish application.Adverse Effects:
When the recommended dosage of Fluoride varnish is followed, no side effects should occur. Inadvertent ingestion can produce headaches and weakness. More severe instances of excessive ingestion can cause CNS problems such as irritability, paresthesia, tetany, convulsion, respiratory failure, and cardiac failure. Fluoride has direct toxic action on nerve tissue.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to fluorides.
Presentation:
Contains 10 tubes of 1.5ml each
-
Hexidine 160ml
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. diluted to chlorhexidine gluconate 0.2% w/v in a pleasantly flavoured base.
Understanding Chlorhexidine gluconate:
1. Chlorhexidine (CHX) is known as the gold standard antiplaque agent because of its persistent attachment and sustained release for long Antiseptic, Antiplaque, Antiviral, Antifungal action.
2. Five decades of evidence for the antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal action.
3. Chlorhexidine’s antiplaque effect is because of its dicationic nature, which confers it the property of substantivity— persistent antimicrobial action through bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects.Mechanism of action:
1. Chlorhexidine is a symmetric bis-biguanide molecule carrying two positive charges at physiological pH. Due to its cationic properties, chlorhexidine binds to negatively charged sites within the plaque biofilm including the bacteria, extracellular polysaccharides, and glycoproteins.
2. The cationic chlorhexidine molecule gets rapidly attracted to the surface of a negatively charged bacterial cell wall, where it binds with specific and strong adsorption to phosphate-containing components of the bacterial cell wall.
3. Due to the strong binding, chlorhexidine passively diffuses through the bacterial cell wall.
4. First, chlorhexidine damages the outer cell membrane compromising the cell integrity, which allows chlorhexidine to infiltrate the inner cell membrane, resulting in greater permeability.
5. This infiltration results in an outflow of low-molecular-weight molecules and cytoplasmic components escaping from the bacterial cell.
6. At this point, chlorhexidine’s antimicrobial action remains bacteriostatic, which can be reversed if chlorhexidine is removed. However, if the chlorhexidine concentration remains stable over time or increases, it can cause irreversible cell damage via bactericidal action.
7. The bactericidal action involves cytoplasmic coagulation and precipitation, where chlorhexidine forms complexes with phosphorylated compounds, such as ATP and nucleic acids.
8. The dicationic chlorhexidine exhibits good adherence to most oral surfaces (including mucous membranes, teeth, and salivary glycoproteins) due to their negative charge, thus interfering with bacterial adhesion, allowing substantivity for up to 12 hours.Chlorhexidine the Gold standard antiplaque agent
1. Chlorhexidine is the gold standard when it comes to substantivity, which explains its superior
anti-plaque effect because of its superior degree of persistence at the tooth surface (hydroxyapatite) or, more correctly, the superior persistence of its antibacterial effect (both bactericidal and bacteriostatic) at the tooth surface.
2. Chlorhexidine comes under Group A mouthwashes with good substantivity (prolonged action) as well as action on a wide spectrum of bacteria. The only category of mouth rinses belonging to this group are bisguanides (Chlorhexidine). The true anti-plaque effect of Chlorhexidine empowers it to replace mechanical cleaning for short periods when tooth brushing is not possible.Indications:
1. Prevention & treatment of gingivitis. For home use between periodontal treatment visits.
2. Minimizing plaque build up in the absence of brushing.
3. Fungal infections of the mouth: oral candidiasis, denture stomatitis.
4. Secondary bacterial infections for aphthous ulcer.
5. Rinsing & gargling for oropharyngeal viral infections.
6. Alveolar osteitis (dry socket) prevention.
7. Reducing viral spread from oropharyngeal region by reducing the viral load
8. As a pre-procedural rinse before dental procedures.
9. Patients undergoing cancer therapy who can not perform mechanical plaque control due to pain and discomfort in the gingiva and oral mucosa.
10. Post-surgical mouthwash: If toothbrushing is not possible due to postoperative pain after any type of oral, periodontal, soft tissue surgery, or extractions, it is recommended that a 1-minute rinse is performed 3 times a day for 7 days or until sutures are removed and oral hygiene in the form of toothbrushing can resume.Directions for use:
1. Recommended only under professional guidance.
2. Recommended twice daily oral rinsing for 30 seconds at least, morning and evening after toothbrushing. Fill the cap up to 10 ml mark and swish in mouth undiluted for 30 seconds at least, and spit out.
3. For best results, rinse at least 30 minutes after toothbrushing, and avoid eating / drinking for at least 30 minutes after rinsing.
4. For denture stomatitis, cleanse and soak dentures in chlorhexidine mouthwash solution for 15 minutes twice daily.
5. Prolonged use may cause temporary staining of teeth, removed by oral prophylaxis. This usually disappears once the treatment is over, or may require scaling/ polishing. However, staining is known to occur only after continuously using for 4 weeks or more.Presentation:
PET bottles of 80ml (2.7 fl.oz.), 160ml (5.41 fl.oz.) with 10ml measuring cap. Plastic bottle of 500 ml (16.9 fl. oz.).
Caution:
Not to be swallowed. For oral use only.
-
Hexidine 500ml
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. diluted to chlorhexidine gluconate 0.2% w/v in a pleasantly flavoured base.
Understanding Chlorhexidine gluconate:
1. Chlorhexidine (CHX) is known as the gold standard antiplaque agent because of its persistent attachment and sustained release for long Antiseptic, Antiplaque, Antiviral, Antifungal action.
2. Five decades of evidence for the antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal action.
3. Chlorhexidine’s antiplaque effect is because of its dicationic nature, which confers it the property of substantivity— persistent antimicrobial action through bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects.Mechanism of action:
1. Chlorhexidine is a symmetric bis-biguanide molecule carrying two positive charges at physiological pH. Due to its cationic properties, chlorhexidine binds to negatively charged sites within the plaque biofilm including the bacteria, extracellular polysaccharides, and glycoproteins.
2. The cationic chlorhexidine molecule gets rapidly attracted to the surface of a negatively charged bacterial cell wall, where it binds with specific and strong adsorption to phosphate-containing components of the bacterial cell wall.
3. Due to the strong binding, chlorhexidine passively diffuses through the bacterial cell wall.
4. First, chlorhexidine damages the outer cell membrane compromising the cell integrity, which allows chlorhexidine to infiltrate the inner cell membrane, resulting in greater permeability.
5. This infiltration results in an outflow of low-molecular-weight molecules and cytoplasmic components escaping from the bacterial cell.
6. At this point, chlorhexidine’s antimicrobial action remains bacteriostatic, which can be reversed if chlorhexidine is removed. However, if the chlorhexidine concentration remains stable over time or increases, it can cause irreversible cell damage via bactericidal action.
7. The bactericidal action involves cytoplasmic coagulation and precipitation, where chlorhexidine forms complexes with phosphorylated compounds, such as ATP and nucleic acids.
8. The dicationic chlorhexidine exhibits good adherence to most oral surfaces (including mucous membranes, teeth, and salivary glycoproteins) due to their negative charge, thus interfering with bacterial adhesion, allowing substantivity for up to 12 hours.Chlorhexidine the Gold standard antiplaque agent
1. Chlorhexidine is the gold standard when it comes to substantivity, which explains its superior
anti-plaque effect because of its superior degree of persistence at the tooth surface (hydroxyapatite) or, more correctly, the superior persistence of its antibacterial effect (both bactericidal and bacteriostatic) at the tooth surface.
2. Chlorhexidine comes under Group A mouthwashes with good substantivity (prolonged action) as well as action on a wide spectrum of bacteria. The only category of mouth rinses belonging to this group are bisguanides (Chlorhexidine). The true anti-plaque effect of Chlorhexidine empowers it to replace mechanical cleaning for short periods when tooth brushing is not possible.Indications:
1. Prevention & treatment of gingivitis. For home use between periodontal treatment visits.
2. Minimizing plaque build up in the absence of brushing.
3. Fungal infections of the mouth: oral candidiasis, denture stomatitis.
4. Secondary bacterial infections for aphthous ulcer.
5. Rinsing & gargling for oropharyngeal viral infections.
6. Alveolar osteitis (dry socket) prevention.
7. Reducing viral spread from oropharyngeal region by reducing the viral load
8. As a pre-procedural rinse before dental procedures.
9. Patients undergoing cancer therapy who can not perform mechanical plaque control due to pain and discomfort in the gingiva and oral mucosa.
10. Post-surgical mouthwash: If toothbrushing is not possible due to postoperative pain after any type of oral, periodontal, soft tissue surgery, or extractions, it is recommended that a 1-minute rinse is performed 3 times a day for 7 days or until sutures are removed and oral hygiene in the form of toothbrushing can resume.Directions for use:
1. Recommended only under professional guidance.
2. Recommended twice daily oral rinsing for 30 seconds at least, morning and evening after toothbrushing. Fill the cap up to 10 ml mark and swish in mouth undiluted for 30 seconds at least, and spit out.
3. For best results, rinse at least 30 minutes after toothbrushing, and avoid eating / drinking for at least 30 minutes after rinsing.
4. For denture stomatitis, cleanse and soak dentures in chlorhexidine mouthwash solution for 15 minutes twice daily.
5. Prolonged use may cause temporary staining of teeth, removed by oral prophylaxis. This usually disappears once the treatment is over, or may require scaling/ polishing. However, staining is known to occur only after continuously using for 4 weeks or more.Presentation:
PET bottles of 80ml (2.7 fl.oz.), 160ml (5.41 fl.oz.) with 10ml measuring cap. Plastic bottle of 500 ml (16.9 fl. oz.).
Caution:
Not to be swallowed. For oral use only.
-
Hexidine 80ml
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. diluted to chlorhexidine gluconate 0.2% w/v in a pleasantly flavoured base.
Understanding Chlorhexidine gluconate:
1. Chlorhexidine (CHX) is known as the gold standard antiplaque agent because of its persistent attachment and sustained release for long Antiseptic, Antiplaque, Antiviral, Antifungal action.
2. Five decades of evidence for the antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal action.
3. Chlorhexidine’s antiplaque effect is because of its dicationic nature, which confers it the property of substantivity— persistent antimicrobial action through bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects.Mechanism of action:
1. Chlorhexidine is a symmetric bis-biguanide molecule carrying two positive charges at physiological pH. Due to its cationic properties, chlorhexidine binds to negatively charged sites within the plaque biofilm including the bacteria, extracellular polysaccharides, and glycoproteins.
2. The cationic chlorhexidine molecule gets rapidly attracted to the surface of a negatively charged bacterial cell wall, where it binds with specific and strong adsorption to phosphate-containing components of the bacterial cell wall.
3. Due to the strong binding, chlorhexidine passively diffuses through the bacterial cell wall.
4. First, chlorhexidine damages the outer cell membrane compromising the cell integrity, which allows chlorhexidine to infiltrate the inner cell membrane, resulting in greater permeability.
5. This infiltration results in an outflow of low-molecular-weight molecules and cytoplasmic components escaping from the bacterial cell.
6. At this point, chlorhexidine’s antimicrobial action remains bacteriostatic, which can be reversed if chlorhexidine is removed. However, if the chlorhexidine concentration remains stable over time or increases, it can cause irreversible cell damage via bactericidal action.
7. The bactericidal action involves cytoplasmic coagulation and precipitation, where chlorhexidine forms complexes with phosphorylated compounds, such as ATP and nucleic acids.
8. The dicationic chlorhexidine exhibits good adherence to most oral surfaces (including mucous membranes, teeth, and salivary glycoproteins) due to their negative charge, thus interfering with bacterial adhesion, allowing substantivity for up to 12 hours.Chlorhexidine the Gold standard antiplaque agent
1. Chlorhexidine is the gold standard when it comes to substantivity, which explains its superior
anti-plaque effect because of its superior degree of persistence at the tooth surface (hydroxyapatite) or, more correctly, the superior persistence of its antibacterial effect (both bactericidal and bacteriostatic) at the tooth surface.
2. Chlorhexidine comes under Group A mouthwashes with good substantivity (prolonged action) as well as action on a wide spectrum of bacteria. The only category of mouth rinses belonging to this group are bisguanides (Chlorhexidine). The true anti-plaque effect of Chlorhexidine empowers it to replace mechanical cleaning for short periods when tooth brushing is not possible.Indications:
1. Prevention & treatment of gingivitis. For home use between periodontal treatment visits.
2. Minimizing plaque build up in the absence of brushing.
3. Fungal infections of the mouth: oral candidiasis, denture stomatitis.
4. Secondary bacterial infections for aphthous ulcer.
5. Rinsing & gargling for oropharyngeal viral infections.
6. Alveolar osteitis (dry socket) prevention.
7. Reducing viral spread from oropharyngeal region by reducing the viral load
8. As a pre-procedural rinse before dental procedures.
9. Patients undergoing cancer therapy who can not perform mechanical plaque control due to pain and discomfort in the gingiva and oral mucosa.
10. Post-surgical mouthwash: If toothbrushing is not possible due to postoperative pain after any type of oral, periodontal, soft tissue surgery, or extractions, it is recommended that a 1-minute rinse is performed 3 times a day for 7 days or until sutures are removed and oral hygiene in the form of toothbrushing can resume.Directions for use:
1. Recommended only under professional guidance.
2. Recommended twice daily oral rinsing for 30 seconds at least, morning and evening after toothbrushing. Fill the cap up to 10 ml mark and swish in mouth undiluted for 30 seconds at least, and spit out.
3. For best results, rinse at least 30 minutes after toothbrushing, and avoid eating / drinking for at least 30 minutes after rinsing.
4. For denture stomatitis, cleanse and soak dentures in chlorhexidine mouthwash solution for 15 minutes twice daily.
5. Prolonged use may cause temporary staining of teeth, removed by oral prophylaxis. This usually disappears once the treatment is over, or may require scaling/ polishing. However, staining is known to occur only after continuously using for 4 weeks or more.Presentation:
PET bottles of 80ml (2.7 fl.oz.), 160ml (5.41 fl.oz.) with 10ml measuring cap. Plastic bottle of 500 ml (16.9 fl. oz.).
Caution:
Not to be swallowed. For oral use only.
-
Hexidine EP 150ml
Read More Quick ViewChlorhexidine Mouthwash IP/BP
Composition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. dilute to chlorhexidine gluconate 0.12% W/V in pleasantly flavored aqueous base.COLOR:
Brilliant Blue & Tartrazine YellowIndications:
- Prevention of plaque in absence of brushing
- Prevention and treatment of gingivitis
- Treatment of oral candidiasis
- Controlling secondary bacterial infections for aphthous ulcers
- Aid in treatment of mouth and throat infections
DIRECTION FOR USE:
For treatment and prevention, swish in your mouth for one minute. Do not rinse, eat or drink thereafter for 20 minutes. Recommended only under professional guidance.DOSE:
10ml, twice a day.STORAGE:
Keep out of direct sun light.WARNING:
NOT TO BE SWALLOWED. FOR ORAL USE ONLY. Brown staining of teeth may be reported, while using the product in some cases. This usually disappears once the treatment is over or may require scaling/polishing. Remove foil before use.
Net content: 150 ml/500 ml
-
Hexidine Fresh Anise 300m..
Read More Quick ViewHexidine Fresh 300 ml (Anise flavour)
Composition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. diluted to Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.2% w/v in a pleasantly flavoured base.Mode of action:
Bacterial plaque produces irritants, which cause gingivitis and periodontitis, ultimately leading to loss of teeth. Chemical control of plaque is achieved effectively with Hexidine Fresh 300ml. As an antimicrobial, Hexidine Fresh 300ml prevents secondary infections arising out of poor oral hygiene.It is particularly useful in effective plaque control for:
- Patients undergoing gum and implant surgeries
Hexidine Fresh 300ml begins its microbicidal effect in 15 seconds after contact and its bacteriostatic action lasts for 12 hours.
Indications:
For therapeutic use post gum surgeries and implant surgeriesDirections for use:
For treatment, swish in the mouth for one minute. Do not rinse your mouth, eat, drink thereafter for 20 minutes. No dilution required. Recommended only under professional guidance.Dose:
10 ml, twice a day for 15 days.Caution:
Not to be swallowed. For oral use only. Brown staining of the teeth may be reported while using the product in some cases. This usually disappears once the treatment is over, or may require scaling/polishing.Special instructions:
Do not use toothpastes immediately after rinsing with Hexidine Fresh 300ml, as it will diminish its effect. Use them first or at a different time of the day, and rinse your mouth thoroughly with water before using Hexidine Fresh 300ml. Avoid tannin containing food and drinks for at least one hour after using Hexidine Fresh 300ml. If symptoms persist, stop using, and consult your dentist. Noticeable change in taste, or burning sensation may occur in exceptional cases upon first use. This usually goes away as you continue to use the product.Presentation:
PET bottle of 300 ml (10.14 oz.) -
Hexigel 15gm
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. equivalent to chlorhexidine gluconate 1.0% w/w in pleasantly flavoured base.
The use of Chlorhexidine gel:
The application of chlorhexidine (CHX) gel on ulcers and wound surfaces after oral surgical procedures has received considerable attention— supported scientifically by the antimicrobial properties of chlorhexidine.
Chlorhexidine acts against bacteria (Gram-positive and Gram-negative), with bacteriostatic action at low concentrations and bactericidal action at high concentrations Chlorhexidine is also known for its antiviral and antifungal effects.Mode of action:
Chlorhexidine acts on the target micro-organisms by increasing their cell membrane permeability which causes the precipitation of cytoplasmic macromolecules and subsequent microbial death via cell lysis. Therefore, the effect of CHX is mainly based on minimizing the microbial load —playing an anti-infection role, which seems critical in the early stages of wound healing.
Indications:
1. Periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis
2. Oral candidiasis, esp denture stomatitis
3. Aphthous and other oral ulcers, such as due to dentures
4. Common oral injuries, including those from orthodontic appliances and oral surgery appliances
5. Maintenance of oral hygiene, especially interdentally — in cancer patients, gingivitis & periodontitis patients, between and around restorationsScientific basis in various clinical applications:
A. Hexigel in the prevention of alveolar osteitis (dry socket)
The extraction of third molars is a common dental procedure. The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons states that “about 85% of third molars will eventually need to be removed”.
Available data also shows that 5 to 30% third molar extractions can create a”dry socket” – a complication associated with severe pain.
How can we prevent this unwanted complication?
1. A meta-analysis published in “Oral Diseases” in August 2016, reviewed 11 trials and found that 0.2% chlorhexidine gel was effective in preventing alveolar osteitis after lower third molar extraction(s).
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/odi.12553
2. Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery in May 2017, reviewed Twenty-three studies published from 1979 to 2015 and concluded that chlorhexidine, used in any formulation and concentration can prevent dry socket in patients who have undergone third molar extraction. https://www.joms.org/article/S0278-2391(17)30020-4/fulltext
3. Another systematic review & meta-analysis published in May 2017 found that Chlorhexidine gel is superior to placebo in reducing the incidence of alveolar osteitis after mandibular third molar extraction.
https://bmcoralhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12903-017-0376-3
4. The largest network meta-analysis done till now reviewed 37 randomized controlled trials that included 6175 mandibular third molar surgeries in 4716 patients. This study published in Sept 2020 showed that 0.2% Chlorhexidine gel placed in the socket can prevent dry socket after mandibular third molar surgery.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1010518220301578
Hexigel, a 1% Chlorhexidine gluconate-based gel, is an inexpensive and easily available local application for all the 3rd molar extraction patients. They can apply it multiple times a day from the day of tooth extraction. A single tube of Hexigel contains enough quantity of gel to give protective coverage during the critical phase of the first couple of days.Use Hexigel after every case of lower molar extraction, especially the surgical extraction of the lower wisdom tooth, and minimize the risk of dry socket.
B. Hexigel as a post-surgical gel
High-quality articles demonstrate the evidence that Chlorhexidine gel application
exerts a beneficial effect on oral surgical wound healing. Chlorhexidine gel
application significantly decreases the risk of surgical complications and/or poor
wound healing.C. Hexigel in denture stomatitis
Denture stomatitis (DS) seen in about 15-70% of denture wearers is a condition characterized by a generalized inflammation of the denture-covered palatal mucosa. The clinical signs can vary from petechiae to generalized inflammation with papillary hyperplasia.
It is a harmless form of oral candidiasis associated with a quantitative increase of yeasts (a mixture of Candida species eg. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. krusei, C. guilliermondii, C. glabrata) on the mucosa and the denture’s fit surface. Complete and removable dentures accumulate, among all, C. albicans on the porous surface of the acrylic resin.
Denture hygiene is an important factor in the prevention and treatment of DS. Chlorhexidine digluconate, an effective antimicrobial agent active against various bacteria, viruses, and fungi including C. albicans, is recommended in the treatment of denture stomatitis because of its proven clinical and microbiological efficacy.
D. Hexigel in cancer patients
Patients can use an interdental brush dipped in chlorhexidine gel to clean the areas between teeth, crowns, and bridges to ensure good oral health.
E. Hexigel in periodontitis patients
Cleaning the interdental areas is a critical component of oral care in periodontitis patients.
F. Hexigel in restorative dentistry
Restorations with overhangs and rough edges can create plaque-retentive areas around the crowns, bridges, and fillings. Cleaning the interdental areas is critical to maintaining soft tissue health interdentally. Cleaning the interdental areas is a critical component of oral care in periodontitis patients.
Directions for use:
For oral hygiene, plaque inhibition and gingivitis: Brush your teeth with the gel once or twice a day. Use an interdental brush for carrying hexigel between teeth, crowns, bridges, and implants. For management of aphthous and other oral ulcers: Apply the gel to affected areas once or twice a day.
Warning:
Brown staining may be reported with extensive use in some cases. It can be removed by brushing or polishing.
Presentation:
Lamitube of 15g (0.52 oz)
-
Heximetro 15gm
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Chlorhexidine Gluconate 1% w/w, Metronidazole 1% w/w, Lignocaine 2% w/w
Introduction:
Heximetro is an antiseptic mouth gel with triple action- that synergistically acts against both —aerobic and anaerobic pathogens in oral lesions, and also provides instant pain relief via topical anaesthesia.
Chlorhexidine:
Chlorhexidine is a well-known antiseptic, and antimicrobial agent with decades of evidence of its antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal action. Chlorhexidine offers action against aerobic pathogens like- S. sanguis, S. mutans (Chlorhexidine- binds with the phospholipids in the innercell membrane causing cell wall integrity). The application of chlorhexidine (CHX) gel on ulcers and wound surfaces after oral surgical procedures has received considerable attention— supported scientifically by the antimicrobial properties of chlorhexidine. Chlorhexidine acts against bacteria (Gram-positive and Gram-negative), with bacteriostatic action at low concentrations and bactericidal action at high concentrations Chlorhexidine is also known for its antiviral and antifungal effects.
Mode of action:
Chlorhexidine acts on the target micro-organisms by increasing their cell membrane permeability which causes the precipitation of cytoplasmic macromolecules and subsequent microbial death via cell lysis. Therefore, the effect of CHX is mainly based on minimizing the microbial load —playing an anti-infection role, which seems critical in the early stages of wound healing.
Metronidazole:
Metronidazole offers action against anaerobic pathogens like- P. gingivalis, etc (inhibits protein synthesis by interacting with DNA, and causes a loss of helical DNA structure and strand breakage)
Lignocaine:
Heximetro also contains 2% Lignocaine, which can provide instant and profound anesthesia over the surfaces of oral lesions.
Indications:
1. Infected painful ulcers in the mouth
2. Periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis with pockets
3. Oral candidiasis, esp painful denture stomatitis lesions
4. Aphthous ulcers
5. Ulcers due to dentures
6. Common oral injuries, including those from orthodontic appliances and oral surgery appliances
7. Dry socket (alveolar osteitis) prevention and treatment
8. Infections in the interdental areas: to be applied with interdental brushes like Thermoseal proxa
9. Maintenance of oral hygiene, especially interdentally — in cancer patients,
gingivitis & periodontitis patients, between and around restorationsHeximetro in various clinical conditions:
A. Heximetro in dry socket:
The extraction of third molars is a common dental procedure. The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons states that “about 85% of third molars will eventually need to be removed”. Available data also shows that 5 to 30% third molar extractions can create a “dry socket” – a complication associated with severe pain.
How can we prevent this unwanted complication?
1. A meta-analysis published in “Oral Diseases” in August 2016, reviewed 11 trials and found that 0.2% chlorhexidine gel was effective in preventing alveolar osteitis after lower third molar extraction(s). https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/odi.12553
2. Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery in May 2017, reviewed Twenty-three studies published from 1979 to 2015 and concluded that chlorhexidine, used in any formulation and concentration can prevent dry socket in patients who have undergone third molar extraction. https://www.joms.org/article/S0278-2391(17)30020-4/fulltext
3. Another systematic review & meta-analysis published in May 2017 found that Chlorhexidine gel is superior to placebo in reducing the incidence of alveolar osteitis after mandibular third molar
extraction. https://bmcoralhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12903-017-0376-34. The largest network meta-analysis done till now reviewed 37 randomized controlled trials that included 6175 mandibular third molar surgeries in 4716 patients. This study published in Sept 2020 showed that 0.2% Chlorhexidine gel placed in the socket can prevent dry socket after mandibular third molar surgery. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1010518220301578
Chlorhexidine in its therapeutic concentration of 1% fortified with an additional metronidazole cover, and lignocaine surface anesthesia, heximetro can ensure the healing of the dry socket.
B. Heximetro as a post-surgical gel
High-quality articles demonstrate the evidence that Chlorhexidine gel application exerts a beneficial effect on oral surgical wound healing. Chlorhexidine gel application significantly decreases the risk of surgical complications and/or poor wound healing. With additional metronidazole cover and lignocaine surface anesthesia, heximetro can ensure uneventful healing.
C. Heximetro in denture stomatitis
Denture stomatitis (DS) seen in about 15-70% of denture wearers is a condition characterized by a generalized inflammation of the denture-covered palatal mucosa. The clinical signs can vary from petechiae to generalized inflammation with papillary hyperplasia. It is a harmless form of oral candidiasis associated with a quantitative increase of yeasts (a mixture of Candida species eg. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. krusei, C. guilliermondii, C. glabrata) on the mucosa and the denture’s fit surface. Complete and removable dentures accumulate, among all, C. albicans on the porous surface of the acrylic resin.
Denture hygiene is an important factor in the prevention and treatment of DS. Chlorhexidine digluconate, an effective antimicrobial agent active against various bacteria, viruses, and fungi including C. albicans, is recommended in the treatment of denture stomatitis because of its proven clinical and microbiological efficacy. Lignocaine can ensure comfortable denture wear by providing surface anesthesia on the inflamed tissue surfaces.D. Hexigel in cancer patients
Patients with sensitive soft tissues can use an interdental brush dipped in Heximetro gel to clean the areas between teeth, crowns, and bridges to ensure good oral health.
E. Hexigel in periodontitis patients
Cleaning the interdental areas is a critical component of oral care in periodontitis patients. Patients with periodontitis can use an interdental brush dipped in Heximetro gel to clean the areas between teeth, crowns, and bridges to ensure good periodontal health.
F. Hexigel in restorative dentistry
Restorations with overhangs and rough edges can create plaque-retentive areas around the crowns, bridges, and fillings. Cleaning the interdental areas is critical to maintaining soft tissue health interdentally.
Dose:
2 to 3 times a day or as directed by the doctor.
Presentation:
15 gms in a lami tube
-
Hexiprep 500ml
Read More Quick ViewMicrobicidal Skin Prepping Solution
Composition:
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Solution 2% v/v, equivalent to Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.4% w/v, in Isopropyl Alcohol base. (Formulation available – I.P. – Domestic, B.P. – Export)Mode of Action:
15 seconds contact microbicidal 12 hours skin binderIndications:
Presurgical preparation and asepsis solution for skin disinfection and for colour demarcation of the area of incision. 66Directions for use:
Apply undiluted solution with clean surgical cotton swab on the skin prior to surgery.Storage:
Protect from heat and light. Keep away from flame. Keep bottle capped when not in use.Caution:
Keep away from eyes and children. For external use only.Presentation:
Plastic bottle of 500ml (16.9 fl.oz). -
Hexiprep T 500ml
Read More Quick ViewMicrobicidal Hand Rub
Composition:
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Solution 2.5% v/v, equivalent to Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.5% w/v in aqueous base. Ethyl Alcohol 70% v/v Perfume: eau de Cologne (Formulation available – I.P. – Domestic, B.P. – Export)
Mode of Action:
15 seconds contact microbicidal 12 hours skin binder.
Indications:
Hand Rub Skin Cleanser Cleaning of wounds, abrasions, minor cuts Barrier Nursing.
Directions for use:
Use undiluted for hand asepsis. Take Hexiprep-T in sufficient quantity and rub gently on dry hands, fingernails, and all surfaces, till it dries.
Storage:
Protect from heat and light. Keep away from flame Keep bottle capped when not in use.
Caution:
Keep away from eyes and children For external use only.
Presentation:
Plastic bottle of 500ml (16.9 fl. oz), with a pump
-
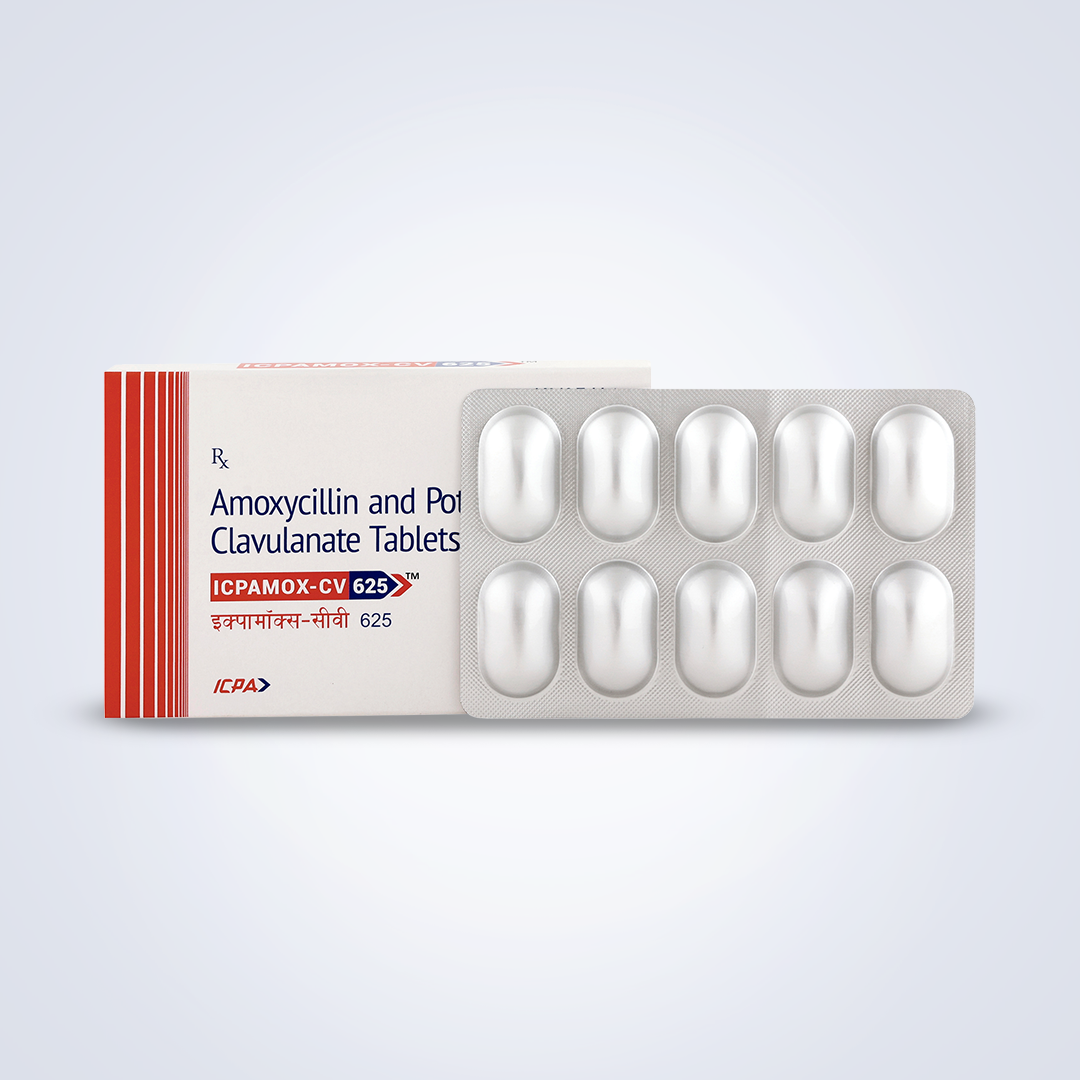
ICPAMOX-CV
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Amoxycillin 500mg + Clavulanic acid 125mg Tablet
Introduction:
ICPAMOX-CV 625 is an antibiotic with broad-spectrum activity against the commonly occurring bacterial pathogens involved in the infections of the oral cavity and other parts of the body. The beta-lactamase inhibitory action of clavulanic acid extends the spectrum of Amoxycillin to act against a wider range of organisms, including many resistant to other beta-lactam antibiotics.
Indications:
ICPAMOX-CV improves treatment success rate in,
1. Acute periapical abscess; along with endo treatment
2. Before starting endo treatment; to reduce post-operative pain
3. Tooth extraction & other oral surgeries; to reduce post-operative infection and bacteremia
4. Before wisdom tooth surgeries; to prevent post-operative infection & dry socket
5. Pericoronitis & Peri-implantitis
6. Periodontitis (as an adjunct to scaling & root planing), periodontal surgeries, periodontal abscess.
7. Facial cellulitisDose:
One tablet BID for 3-7 Days.
Presentation:
Alu Alu blister pack of 10 tablets
Common side effects:
- Diarrhea
- Stomach upset
- Nausea and vomiting
- Mild skin rash
-
Icparil Tab 10’s
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Each uncoated tablet contains: Paracetamol 325mg Aceclofenac 100mgMode of Action:
Aceclofenac relieves pain and inflammation through a variety of mechanisms and in addition exerts stimulatory effects on cartilage matrix synthesis.
Paracetamol is a clinically proven analgesic and antipyretic agent with weak inflammatory effect. Paracetamol produces analgesia by raising pain threshold. And inhibits COX in CNS and exerts antipyretic action.Indications:
All inflammatory & painful conditions Pre & Post – extraction of teeth Rheumatoid arthritis Spondylitis Osteoarthritis Low back pain Periarthritis of shoulders Other musculoskeletal and joint disorders such as sprains & strains Pelvic inflammation Post – operative pain DysmenorrheaCaution:
Paracetamol overdose may cause liver failure.Dose:
One tablet twice a day or as directed by the physician.Presentation:
Blister pack of 10 Tablets.
Quick Links
Our Products
Information
Contact us
- 216-219, Adarsh Industrial Estate, Sahar Road, Chakala, Andheri (East), Mumbai - 400099
- Fax : 28216928
- +91 22 40065305 / 40065306 / 40065307
- info@icpahealth.com

Selected Icpa Products
Click on Add to cart to add this item in cart.
| PRODUCTS | QTY | PRICE | VALUE in INR |
|---|
Selected Icpa Products
Click on Add to cart to add this item in cart.
| PRODUCTS | QTY | PRICE | VALUE in INR |
|---|