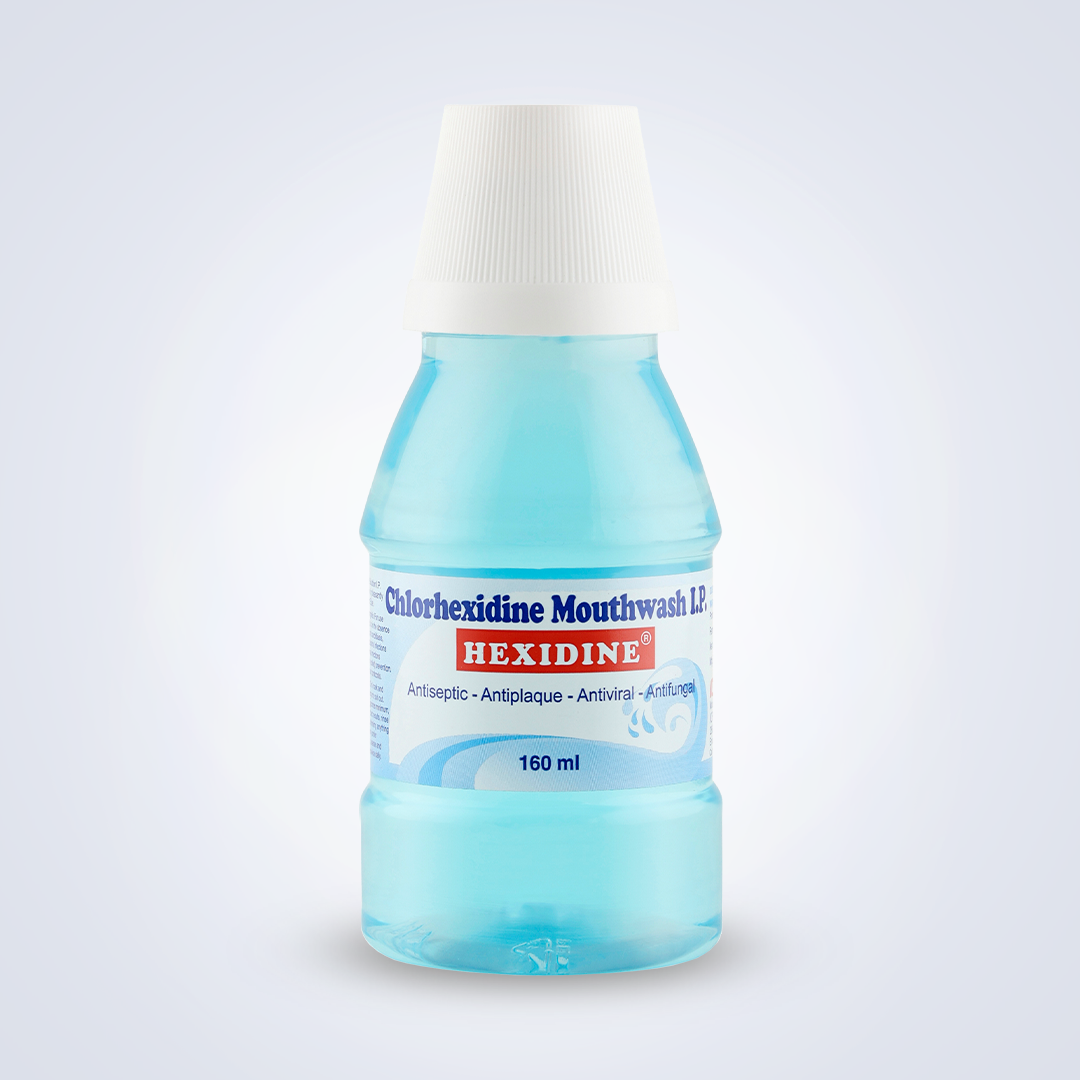
Hexidine 160ml
Hexidine 160ml
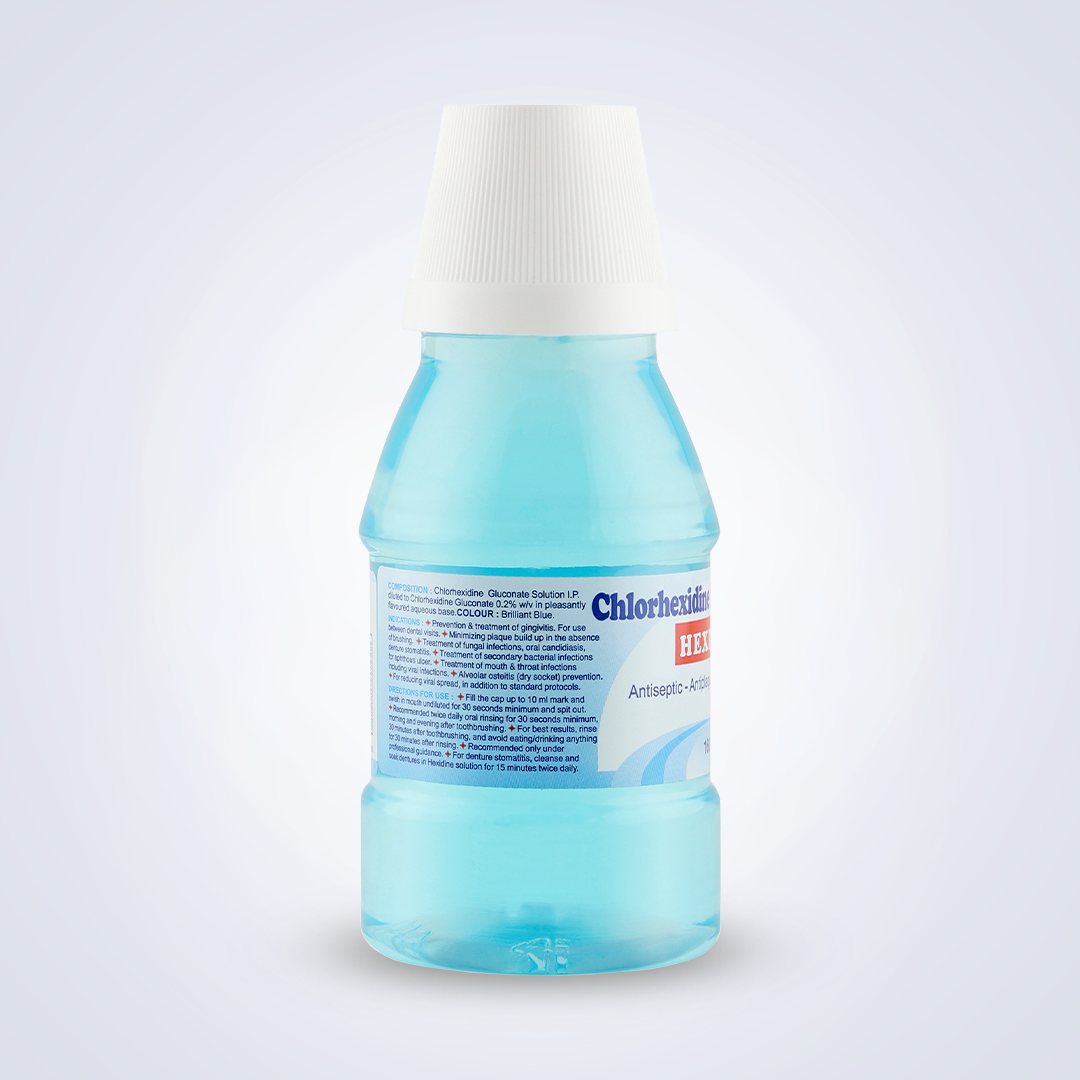
Composition:
Chlorhexidine gluconate solution I.P. diluted to chlorhexidine gluconate 0.2% w/v in a pleasantly flavoured base.
Understanding Chlorhexidine gluconate:
1. Chlorhexidine (CHX) is known as the gold standard antiplaque agent because of its persistent attachment and sustained release for long Antiseptic, Antiplaque, Antiviral, Antifungal action.
2. Five decades of evidence for the antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal action.
3. Chlorhexidine’s antiplaque effect is because of its dicationic nature, which confers it the property of substantivity— persistent antimicrobial action through bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects.
Mechanism of action:
1. Chlorhexidine is a symmetric bis-biguanide molecule carrying two positive charges at physiological pH. Due to its cationic properties, chlorhexidine binds to negatively charged sites within the plaque biofilm including the bacteria, extracellular polysaccharides, and glycoproteins.
2. The cationic chlorhexidine molecule gets rapidly attracted to the surface of a negatively charged bacterial cell wall, where it binds with specific and strong adsorption to phosphate-containing components of the bacterial cell wall.
3. Due to the strong binding, chlorhexidine passively diffuses through the bacterial cell wall.
4. First, chlorhexidine damages the outer cell membrane compromising the cell integrity, which allows chlorhexidine to infiltrate the inner cell membrane, resulting in greater permeability.
5. This infiltration results in an outflow of low-molecular-weight molecules and cytoplasmic components escaping from the bacterial cell.
6. At this point, chlorhexidine’s antimicrobial action remains bacteriostatic, which can be reversed if chlorhexidine is removed. However, if the chlorhexidine concentration remains stable over time or increases, it can cause irreversible cell damage via bactericidal action.
7. The bactericidal action involves cytoplasmic coagulation and precipitation, where chlorhexidine forms complexes with phosphorylated compounds, such as ATP and nucleic acids.
8. The dicationic chlorhexidine exhibits good adherence to most oral surfaces (including mucous membranes, teeth, and salivary glycoproteins) due to their negative charge, thus interfering with bacterial adhesion, allowing substantivity for up to 12 hours.
Chlorhexidine the Gold standard antiplaque agent
1. Chlorhexidine is the gold standard when it comes to substantivity, which explains its superior
anti-plaque effect because of its superior degree of persistence at the tooth surface (hydroxyapatite) or, more correctly, the superior persistence of its antibacterial effect (both bactericidal and bacteriostatic) at the tooth surface.
2. Chlorhexidine comes under Group A mouthwashes with good substantivity (prolonged action) as well as action on a wide spectrum of bacteria. The only category of mouth rinses belonging to this group are bisguanides (Chlorhexidine). The true anti-plaque effect of Chlorhexidine empowers it to replace mechanical cleaning for short periods when tooth brushing is not possible.
Indications:
1. Prevention & treatment of gingivitis. For home use between periodontal treatment visits.
2. Minimizing plaque build up in the absence of brushing.
3. Fungal infections of the mouth: oral candidiasis, denture stomatitis.
4. Secondary bacterial infections for aphthous ulcer.
5. Rinsing & gargling for oropharyngeal viral infections.
6. Alveolar osteitis (dry socket) prevention.
7. Reducing viral spread from oropharyngeal region by reducing the viral load
8. As a pre-procedural rinse before dental procedures.
9. Patients undergoing cancer therapy who can not perform mechanical plaque control due to pain and discomfort in the gingiva and oral mucosa.
10. Post-surgical mouthwash: If toothbrushing is not possible due to postoperative pain after any type of oral, periodontal, soft tissue surgery, or extractions, it is recommended that a 1-minute rinse is performed 3 times a day for 7 days or until sutures are removed and oral hygiene in the form of toothbrushing can resume.
Directions for use:
1. Recommended only under professional guidance.
2. Recommended twice daily oral rinsing for 30 seconds at least, morning and evening after toothbrushing. Fill the cap up to 10 ml mark and swish in mouth undiluted for 30 seconds at least, and spit out.
3. For best results, rinse at least 30 minutes after toothbrushing, and avoid eating / drinking for at least 30 minutes after rinsing.
4. For denture stomatitis, cleanse and soak dentures in chlorhexidine mouthwash solution for 15 minutes twice daily.
5. Prolonged use may cause temporary staining of teeth, removed by oral prophylaxis. This usually disappears once the treatment is over, or may require scaling/ polishing. However, staining is known to occur only after continuously using for 4 weeks or more.
Presentation:
PET bottles of 80ml (2.7 fl.oz.), 160ml (5.41 fl.oz.) with 10ml measuring cap. Plastic bottle of 500 ml (16.9 fl. oz.).
Caution:
Not to be swallowed. For oral use only.
Only for Doctors
Compare











Dr. Om prakash –
Hexidine is gives best result as antiseptic & anti plaque
Dr Nimai Chandra Dey –
It gives a unique freshness in breathing and mouth. However for plaque prevention, it requires more time to use.
aloke ghosh –
This is the best mouthwash against any kind of infections inside the mouth, including blisters of all sorts on the mucus membranes in side the mouth and lips.