Menu
Date: 1st. Sept. 2017
Let us continue our discussion about management techniques for bleeding in the dental clinic. Previously we have discussed innovative methods that would aid the clinician manage episodes of bleeding in his clinic.
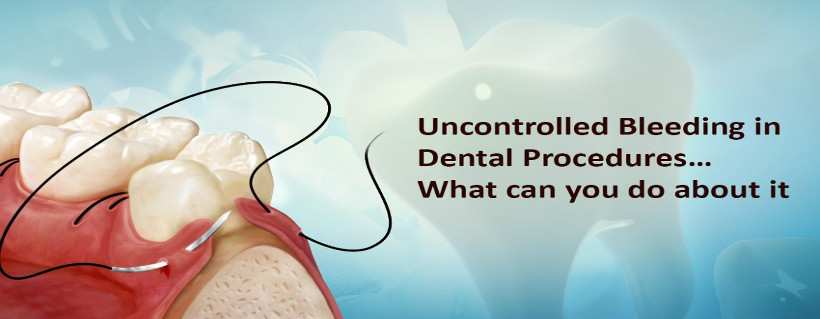
Let us talk about another valuable remedy that every clinician can use in his or her practice to control bleeding. This technique is suturing.
Suturing means to use a strand or thread of material to approximate tissues or flap edges together and hold them in apposition until normal healing takes place.
1] To decrease the size of the said wound /wounds
2] To prevent food lodgement in the said area
3] To promote oral hygiene and reduce bacterial count in the area
4] To speeden up the process of recovery after surgery.
A basic discussion about sutures are that they are classified into 2 categories that is ABSORBABLE and NON ABSORBABALE.
Absorbable sutures are further classified as – Natural and Synthetic.
Non-absorbable sutures are classified as – Natural, Metallic and Synthetic.
Various sutures can be used for intra oral use. The surgeon should make his selection based on a suture that will lose its tensile strength at about the same rate that the tissues gain strength. In slow healing tissues, non-absorbable sutures are used whereas in rapidly healing tissues absorbable sutures are used. In cancer patients, hypoproteinemia and chemotherapy can cause breakdown of wounds thus synthetic non-absorbable sutures can be used. If the patient has to be irradiated in the post-operative period polyester material is to be used. In malnourished patients, non-absorbable sutures are the obvious material of choice as tissues need to be approximated for a longer period of time. Thus, suturing provides a valuable tool to control bleeding in the clinic.
Over the years dentistry has increased its scope of treatment thus enabling patients to get solutions to problems they never knew existed in the past. Modern dentistry has added many new vistas to dental treatment in the form of various gadgets which allow the clinician to execute predictable and accurate treatment protocols.
ELECTROSURGERY:
An electrosurgical device allows the operator to perform treatments that would necessarily result in excessive bleeding to very less or almost no blood at all. It involves application of an electrically generated heat to tissue to alter it for therapeutic purposes. Thus the major uses of electrosurgery in dentistry to control bleeding and encourage uneventful post-operative healing are
FRENECTOMY:
It is a treatment to remove the frenum both labial/or lingual .It is done in conventional orthodontic therapy for diastema closure. A diastema is a space in the midline between the two central incisors. One of the etiologies is a high frenal attachment. Thus once the midline space is closed by conventional orthodontic therapy to prevent a relapse, an electrosurgical frenectomy can be performed to give a bloodless result and hasten healing.
GINGIVECTOMY:
It is the excision of gingival for various esthetic and therapeutic purposes. Conventionally it would result in lot of buccal gingival bleeding this technique is very operator friendly.
OPERCULOECTOMY:
In posterior areas like lower third molar teeth this procedure is use to uncover the flap and this eliminate pericoronitis.
SOFT TISSUE UNCOVERING:
In some children where there is delayed eruption and the dentist himself must uncover the teeth this technique helps to reduce bleeding as well as reduces the apprehension of the pediatric patients.
GINGIVOPLASTY:
Minor changes to improve the appearance or health of gums can be carried out by this procedure.
PULPOTOMY:
It is a procedure performed in pediatric patients where the dental pulp gets exposed either due to dental caries or due to a mechanical exposure. The pulp being vital bleeds a lot. In this case electrosurgery can control the bleeding and allow the clinician to place a medicament and complete the procedure, thus saving valuable chair side time and improving vision while working. Also since bleeding is controlled, integrity of the medicament is enhanced.
Sealing of Perforation While Doing Root Canal Treatments:
In cases, where the pulp chamber has undergone a lot of calcification, it is difficult to locate the canals and many a times the dentist lands up in a perforation. This perforation is a direct communication between the tooth and the bone. Therefore, it needs to be sealed. Unfortunately, due to persistent bleeding in this area, it is very difficult to locate the canals and differentiate it from the perforation. Thus, by electrosurgery, we can control the bleeding in the perforation first, locate the canals, place instruments in the canals so as to obliterate the canal space and then the perforation can be sealed using Biodentine or Mineral Trioxide Aggregate.
This procedure if performed as soon as a perforation is detected will greatly improve the prognosis.
INCISION OF PERIODONTAL ABSCESSES: : Conventionally periodontal abscess incision causes uncontrolled bleeding thus electrosurgery can offer a new vista of treatment.
GINGIVAL MELANIN DEPIGMENTATION: : in some patients, there is hyper pigmentation of the gingival which is a cause of esthetic concern to them. Previously a scalpel was the only option. Now electrosurgery provides a cleaner field and better healing.
REMOVAL OF GINGIVAL POLYP: A polyp when excised would cause lot of hemorrhage. Thus, this technique would provide a cleaner field.
(To be continued…)

| PRODUCTS | QTY | PRICE | VALUE in INR |
|---|
| PRODUCTS | QTY | PRICE | VALUE in INR |
|---|
One thought on “Uncontrolled Bleeding in Dental Procedures: Use of Sutures”
Great and useful