Dental Products
Dental Products
Showing 25–35 of 35 results
-
Thermoseal Ortho Toothbru..
Read More Quick View- Thermoseal ortho brush is a professionally designed orthodontic brush with 0.008 inch diameter bristles.
- Long outer bristles of 10 mm gently massage the gums and clean tooth surfaces, while removing plaque from the gum line.
- Short inner bristles of 9.5mm height help clean between braces and teeth efficiently.
- Each 0.008 inch diameter bristle is round-ended to protect enamel and gums.
-
Thermoseal Proxa (WS)
Read More Quick ViewInterdental brushes for cleaning the spaces between teeth, crowns, bridges, braces, and appliances, implants. Improved plastic-coated wire will ensure smooth inward and outward movement and better cleaning of interdental spaces. Rubber grip handle to avoid accidental slips.
Directions for use:
1. While using either a wide space or narrow space brush, insert it carefully between your teeth. Do not force the brush into small openings.
2. Begin at the back of your mouth and on the outside row of teeth. Use repeated in and out motions in each interdental space. Do not use a twisting motion. Repeat procedure from the inside row of teeth, wherever the space permit.
3. Rinse mouth after use and brush with your regular toothbrush.
4. Wash your Thermoseal Proxa Interdental Brush after use.
5. Change your Thermoseal Proxa Interdental brush every weekPresentation:
Each pack of Thermoseal Proxa contains 5 interdental brushes. Available in two packs NS (Narrow Space) & WS (Wide Space).
-
Thermoseal Repair 100gm
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
10% Strontium Chloride Hexahydrate (100 gm)
Understanding tooth wear:
Tooth wear, also known as tooth surface loss, is a common dental condition that affects people of all ages. This silent yet pervasive problem occurs when the hard outer layer of teeth, called enamel, gradually erodes, leaving teeth susceptible to a range of dental issues.
Today, it is becoming evident that erosion initiates the process of dentinal tubule opening, which is then amplified by abrasion, attrition, or abfraction.
Causes of Tooth Wear
Tooth wear can be attributed to a variety of factors, both intrinsic and extrinsic. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and management. Here are some of the primary causes:
1. Acid Erosion: Acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, sodas, and wine, can soften and gradually erode tooth enamel. Frequent consumption of these items can lead to acid erosion.
2. Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): The habit of grinding or clenching teeth, often during sleep, can cause excessive wear on tooth surfaces. Bruxism may be related to stress or misaligned teeth.
3. Abrasion: Mechanical factors like aggressive tooth brushing, using a hard- bristled toothbrush, or abrasive toothpaste can lead to enamel erosion over time.
4. Attrition: Natural tooth-to-tooth contact during activities like chewing and biting can cause wear at contact points. This is more common among individuals with malocclusion (misaligned teeth).
5. Abfraction: Microfractures at the gumline can occur due to excessive pressure during biting and chewing, contributing to tooth wear.Types of Tooth Wear
Tooth wear can manifest in different forms, and understanding these types is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment:
1. Erosion: Acid erosion is characterized by the gradual dissolution of tooth enamel due to acidic substances. It often leads to the exposure of dentin, the softer layer beneath the enamel.
2. Abrasion: External mechanical factors like toothbrush abrasion or abrasive toothpaste result in the wearing away of enamel, primarily at the tooth’s surface.
3. Attrition: The natural wearing of tooth surfaces due to contact between upper and lower teeth during chewing and biting.
4. Abfraction: This type of tooth wear typically appears as wedge-shaped notches at the gumline and is attributed to excessive forces on teeth.Symptoms of Tooth Wear
Tooth wear often progresses silently, making it essential to recognize the signs and symptoms:
1. Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages can be a common early sign of tooth wear.
2. Discoloration: Enamel erosion may lead to teeth appearing discolored, with the underlying dentin showing through.
3. Rough Tooth Edges: Tooth surfaces can become rough and uneven, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup and decay.
4. Fractures and Chips: Weakened enamel is more prone to chipping and fracturing.Preventing Tooth Wear
Prevention is the best approach to managing tooth wear. Here are some strategies to safeguard your enamel:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
2. Dietary Awareness: Limit consumption of acidic foods and beverages, and rinse your mouth with water after consumption.
3. Mouthguards: If you grind your teeth, consider wearing a custom-fitted mouthguard to protect your teeth during sleep.
4. Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings, allowing early detection and intervention if tooth wear is identified.Thermoseal Repair addresses toothwear:
Thermoseal Repair meets the challenges of tooth wear and tear and your patients
will have a refreshing experience daily.
Tooth wear and tear due to daily acid attack is now a common occurrence, in fact 1 out 3 adult suffers from enamel erosion. Studies have shown that consumption of carbonated drinks once daily increases risk of erosion by 2.3 times and risk rises to 5.1 times when the consumption is 4 times daily.
A comparative in vitro, single-blind study, divided 80 randomly selected extracted teeth into 4 groups
Group 1 – 20 teeth acid-etched only; (Control)
Group 2 – 20 teeth treated with strontium chloride;
Group 3 – 20 teeth treated with Biodentine®;
Group 4 – 20 treated with Biodentine® and diode laser.
The samples underwent Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis to check dentinal tubule occlusion.
The qualitative analysis showed no occlusion of dentinal tubules in Group 1 (control group). Dentinal tubule occlusion was 91.2% in strontium chloride group, 81.3% in Biodentine® group and 80.0% in Biodentine® with diode laser group.Why Thermoseal Repair?
1. Thermoseal Repair toothpaste is an improved formulation fortified with the advantage of Strontium chloride hexahydrate.
2. Strontium chloride hexahydrate is in hydrous form, less viscous, hence more Srions available to dentinal tubules.
3. Thermoseal Repair, Repairs and protects as it replaces lost calcium and forms Strontium calcium apatite complex which is acid resistant, hence prevents tooth wear due to acid attack.
4. It is available with good foam, has elegant packing with refreshing fresh mint flavour.
5. Thermoseal Repair offers all contemporary benefits with huge cost savings to your patients. Is available at just 1/3 rd the price of all the competitors.Benefits of Thermoseal Repair:
- Repairs and protects teeth by replacing lost calcium
- Forms strontium calcium apatite complex which is acid resistant, hence prevent tooth wear due to acid attack
- Prevents further tooth wear and tear
- Thermoseal treats and prevents hypersensitivity
Ideal for patients who ask for a good toothpaste for daily use. They can continue with their fluoridated toothpaste. Add Thermoseal Repair as the Good Night toothpaste.
-
Thermoseal Repair 50gm
Read More Quick ViewICPA’s New Launch – Thermoseal Repair
Tooth wear and tear due to daily acid attack is now a common occurrence, in fact 1 out 3 adult suffers from enamel erosion. Studies have shown that consumption of carbonated drinks once daily increases risk of erosion by 2.3 times and risk rises to 5.1 times when the consumption is 4 times daily.
To address this challenge ICPA launches Thermoseal Repair.
-Thermoseal Repair toothpaste is an improved formulation fortified with the advantage of Strontium chloride hexahydrate.
-Strontium chloride hexahydrate is in hydrous form, less viscous, hence more Sr ions available to dentinal tubules.
-Thermoseal Repair, Repairs and protects as it replaces lost calcium and forms Strontium calcium apatite complex which is acid resistant, hence prevents tooth wear due to acid attack.
-It is available with good foam, has elegant packing with refreshing fresh mint flavour.
-Thermoseal Repair offers all contemporary benefits with huge cost savings to your patients. Is available at just 1/3 rd the price of all the competitors.
Thermoseal Repair, besides sensitivity meets the challenges of Tooth wear and tear and your patients will have a refreshing experience daily.
Looking for your experience of Tooth wear specialist – Thermoseal Repair.
-
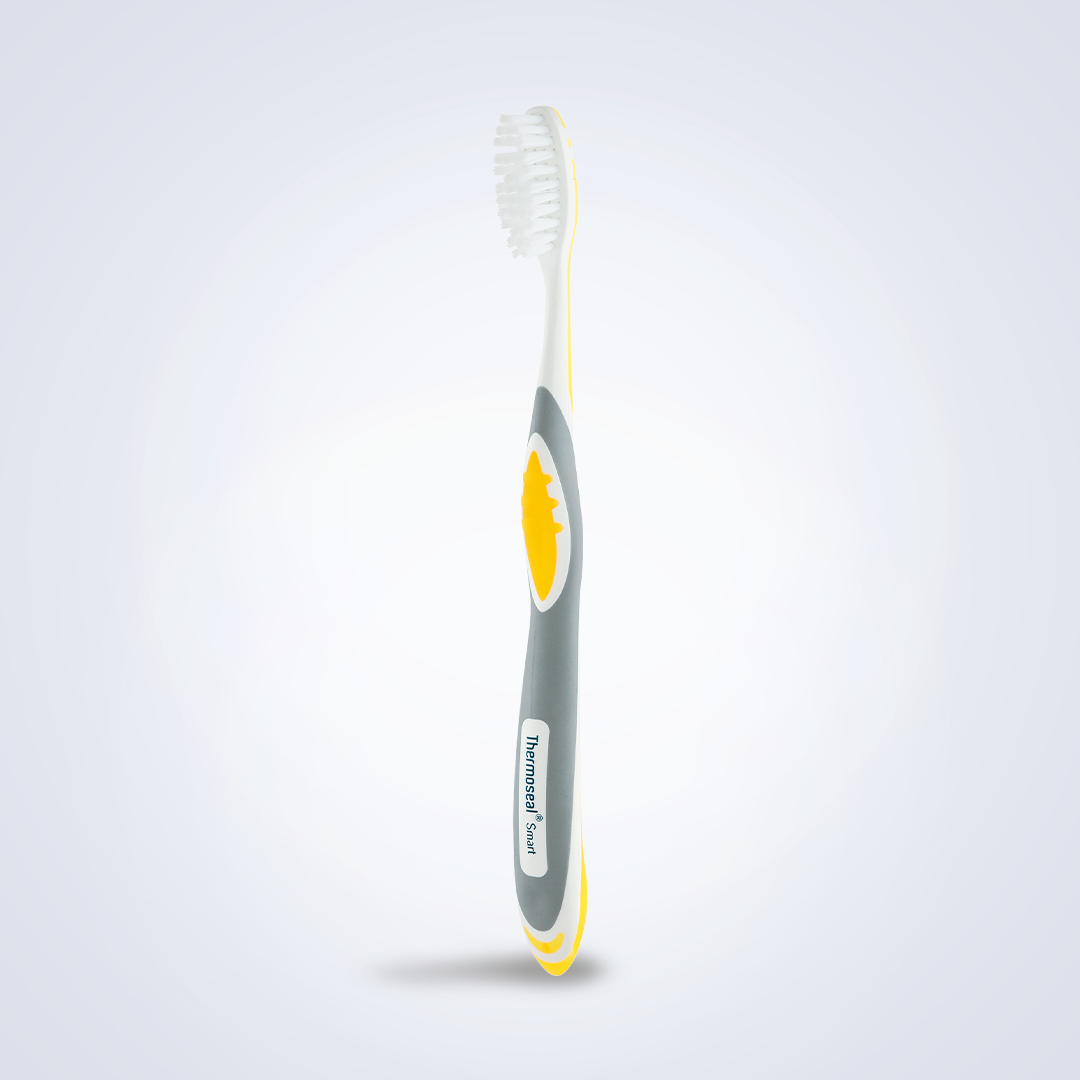
Thermoseal Smart Toothbru..
Read More Quick ViewCleans Areas Difficult to Reach
THERMOSEAL® Smart: Designed to Make Brushing Easier
Thermoseal – Smart
Toothbrush with contoured head to ensure better cleaning and a thumb-grip handle for enhanced grip.
-
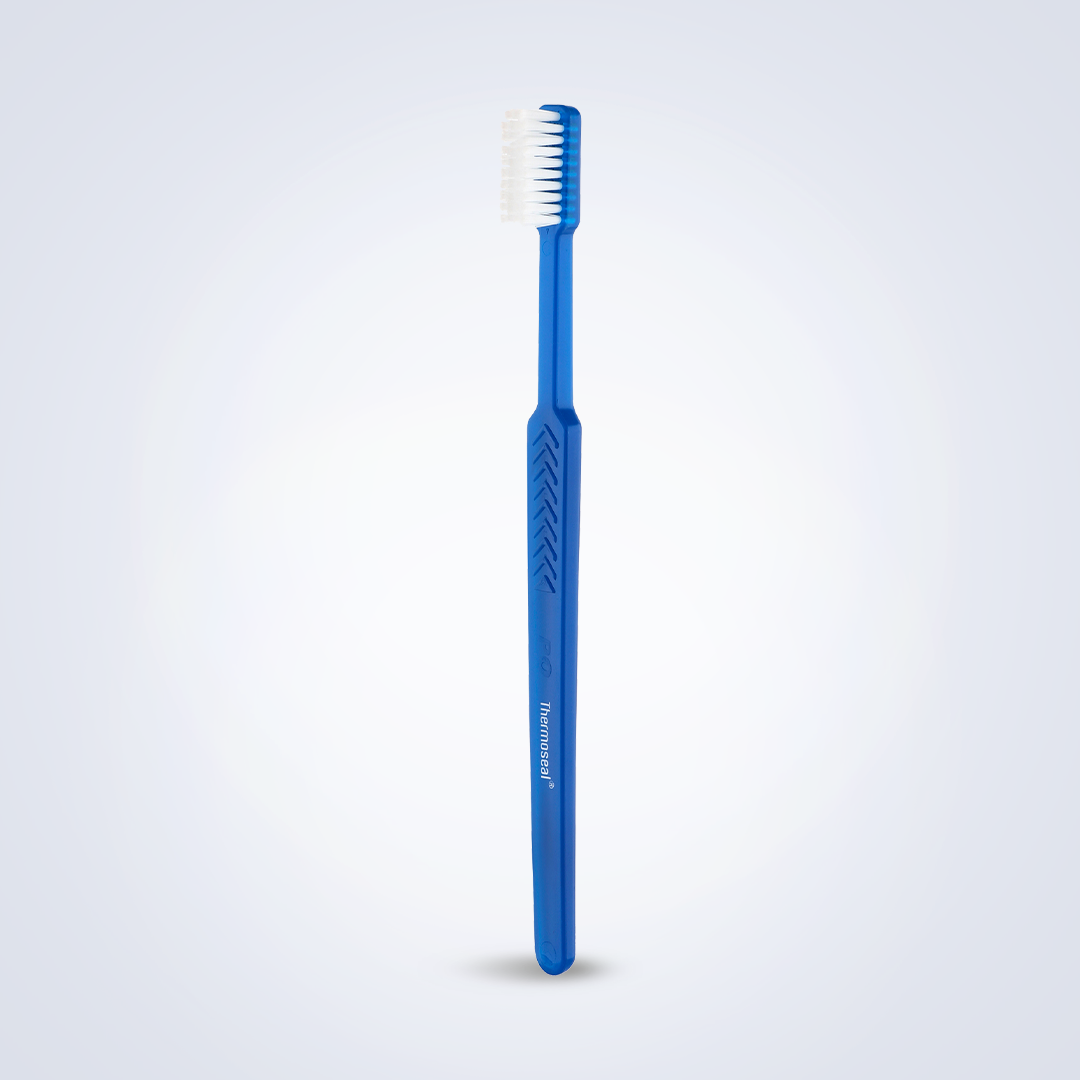
Thermoseal Toothbrush PO
Read More Quick ViewCleans Areas Difficult to Reach
THERMOSEAL® Toothbrush: Cleans Areas Difficult to Reach
Thermoseal – Toothbrush
End-rounded, DuPont bristles with tightly packed tufts and small head. Specially designed for easy brushing.
-
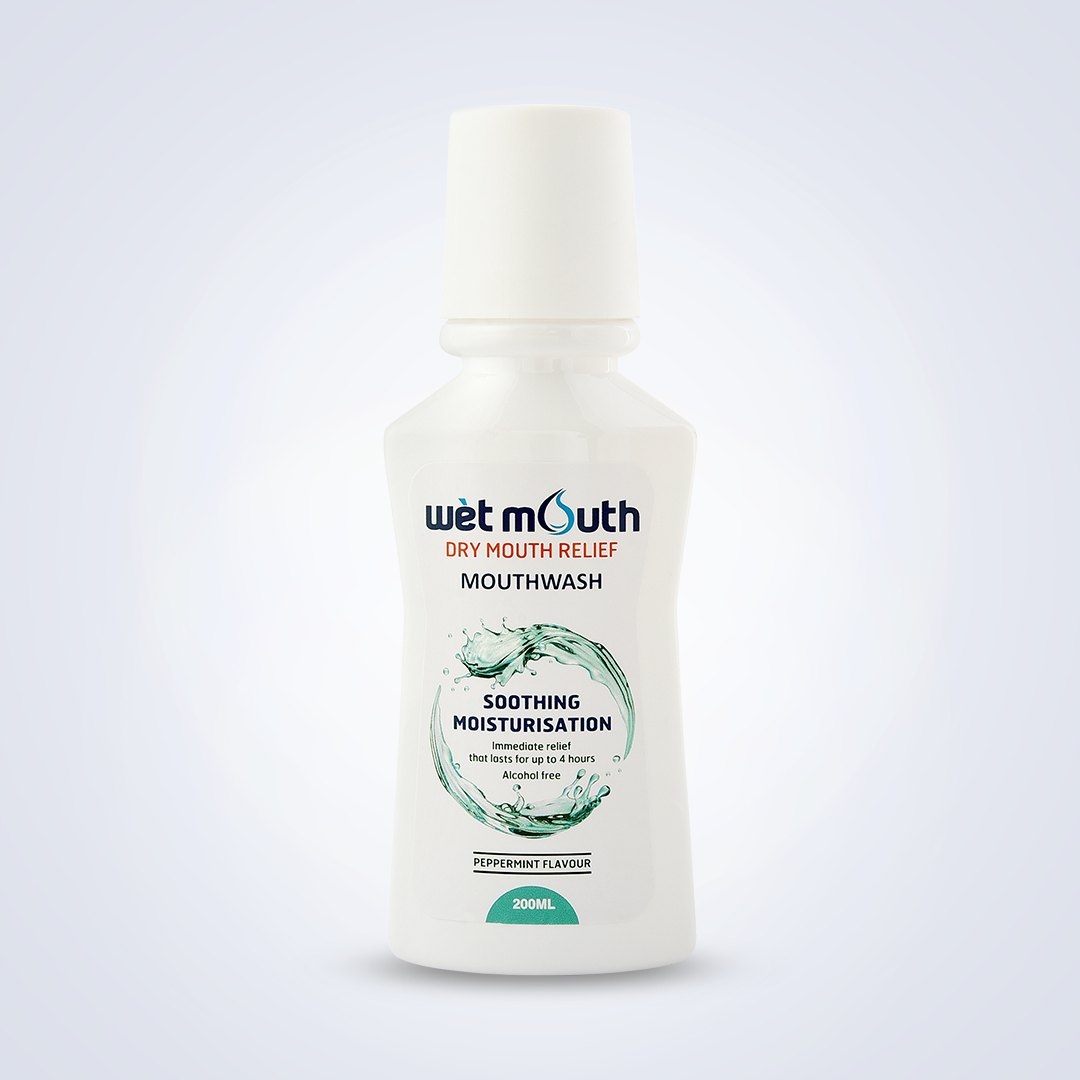
Wet Mouth 200ml New
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Water, Glycerin, Sorbitol, Propylene Glycol, PEG 40 HCO, Poloxamer, Sodium Benzoate, Sodium CMC, Flavour, Cetylpyridinum chloride, parabens, Xylitol, Xanthan gum, Disodium hydrogen phosphate & Sodium dihydrogen Phosphate.
Mode of Action:
With their main action of hydration of oral mucosal tissues, saliva substitutes are useful agents for the palliative management of xerostomia. When used regularly, they keep oral mucosa moist and lubricated. Surface abrasion is reduced and patients can perform everyday activities of eating, sleeping, and speaking.
Causes of dry mouth:
Dry mouth can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Medications: Dry mouth is a common side effect of many prescription and nonprescription drugs. These drugs encompass those used to treat conditions such as depression, anxiety, pain, allergies, colds (such as antihistamines and decongestants), obesity, acne, epilepsy, hypertension (diuretics), diarrhea, nausea, psychotic disorders, urinary incontinence, asthma (specific bronchodilators), Parkinson’s disease, and muscle relaxants and sedatives.
2. Diseases and infections: Certain medical conditions, like Sjögren’s syndrome, HIV/AIDS, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, anemia, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and mumps, can result in dry mouth as a side effect.
3. Medical treatments: Damage to the salivary glands, responsible for saliva production, can reduce saliva output. This damage may occur due to radiation therapy to the head and neck or chemotherapy for cancer treatment.
4. Nerve damage: Nerve damage in the head and neck area, often resulting from injury or surgery, can lead to dry mouth.
5. Dehydration: Conditions causing dehydration, such as fever, excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, blood loss, and burns, can contribute to dry mouth.
6. Salivary gland removal: Surgical removal of the salivary glands can lead to dry mouth.
7. Lifestyle Factors: Smoking or chewing tobacco can reduce saliva production and worsen dry mouth. Frequent mouth breathing can also be a contributing factor.Indications:
Xerostomia, Salivary dysfunction.
Directions for use:
Follow the instructions on the label. Use 15 ml using a measuring cup cum cap. Rinse thoroughly in the mouth for 30 seconds and spit out. DO NOT SWALLOW. Use a maximum of up to 5 times a day depending on individual requirements.
Presentation:
Plastic bottle of 200 ml.
-
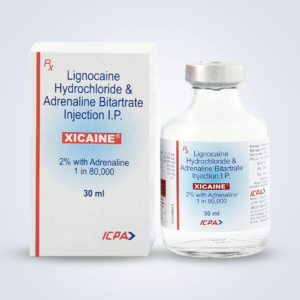
Xicaine Vials (Pack of 20..
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Lignocaine Hydrochloride I.P. 2% Adrenaline I.P. 1:80,000
Mode of Action:
Local anesthetics reversibly block nerve transmission, when applied to a limited area of the body. They bind to the sodium channels in the nerve membrane and prevent the entry of sodium ions in response to the membrane’s depolarization. A vasoconstrictor like Adrenaline added to a local anesthetic may significantly prolong the anesthetic’s duration of action by reducing the blood flow around the injection site. This in turn may reduce the local anaesthetic’s peak plasma concentration and the risk of adverse systemic reactions.
Indications:
Local anesthesia by infiltration or nerve block injection.
Contraindications:
Xicaine is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to local anesthetic of the amide type or the presence of vasoconstrictor. Adrenaline is contraindicated in patients with arterial hypertension, coronary disease, and valvular cardiac disease.
Dosage and administration:
Adults: 2 ml is generally sufficient. 4 to 6 ml may be used if deemed necessary for prolonged procedures.
Adolescents between 14 to 17 and the elderly: The usual dose is 1.8 ml. Do not exceed 3.75 ml.
Children between 6 and 14: The usual dose is 1 to 1.5 ml. Do not exceed 2.5 ml.Caution:
Do not use under 3 years of age.
Storage:
Store in a cool dark place.
Presentation:
Vial of 30 ml (1.01 fl. oz)
-
XTAR 100gm
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Potassium pyrophosphate, sodium pyrophosphate in a combined concentration of 5%. Plus, sodium fluoride 0.24% equivalent to 900 ppm
Understanding Pyrophosphates:
A. Tooth whitening by removal of extrinsic stains caused by tea, coffee, other beverages:
Tooth brushing is the most convenient and economical procedure to remove plaque and extrinsic stains regularly via daily home care. Using tooth-whitening toothpaste for stain removal is becoming increasingly popular.
Types of tooth-whitening toothpastes:
A. Mechanical:
Toothpastes containing abrasive agents, such as charcoal, hydrated silica, or alumina particles can remove tooth stains by mechanical abrasion. Many factors, such as the morphology, particle size, hardness, quantity of abrasive agents, and the amount of toothpaste used— significantly influence the effectiveness of stain removal.
B. Chemical:
Studies have shown that chemical agent containing whitening toothpastes can produce a similar whitening effect compared with hard abrasive toothpastes. An advantage is that the chemically acting whitening toothpastes produce lower surface roughness compared to hard abrasive particle containing whitening toothpastes.
Enzymes, antitartar compounds, and peroxides can help remove extrinsic stains. However, peroxide chemicals remain highly controversial regarding their safety and side effects.
Antitartar agents, such as pyrophosphates, are safer options commonly used as whitening agents.Pyrophosphates as the tooth whitening, stain-removal agents:
- Pyrophosphates are among the ingredients found in whitening toothpastes, which aim to remove extrinsic stains and prevent their reformation.
- Pyrophosphates tend to have strong binding affinity for enamel, dentine and tartar surfaces, and during adsorption they desorb the stain components.
- Pyrophosphates can bind with protein pellicles, preventing incoming stain-attached salivary proteins from adhering to the tooth surface.
B. Calculus formation:
Calculus formation is a common occurrence. Gingivitis and periodontitis were initially linked to the buildup of dental calculus. However, extensive in vivo research has revealed that biofilm plays a more crucial role in the development of these diseases.
Dental calculus results from the mineralization of bacterial plaque and poses a significant challenge to oral health. It exacerbates plaque and bacterial toxins accumulation and hinders their effective removal due to its rough surface. This, in turn, complicates proper hygiene maintenance and promotes further plaque buildup.
Several factors contribute to calculus formation. These factors encompass increased retention of bacterial plaque, biochemical elements like saliva and crevicular fluid composition, the characteristics of the microorganisms within the plaque, and dietary factors.
Notably, dental calculus accumulation varies widely among individuals and is not uniform across the population. Some individuals, even with good plaque control, experience rapid calculus buildup. This necessitates more frequent dental visits and complicates the management of periodontal issues.
Pyrophosphates as anti-tartar/ anti-calculus agents:
- When toothpaste containing the soluble tetra sodium/ potassium pyrophosphate is applied to the teeth and gums, a chemical bonding process occurs.
- Pyrophosphates (crystal growth inhibitor) act as chelating agent and removes calcium from the saliva to form a soluble complex that can be rinsed away with water thereby controlling new calculus buildup.
- Any calcium phosphate that has not yet bonded to teeth is attracted to the sodium pyrophosphate. When the new compound mixes with water, it is completely dissolved.
- The toothpaste cannot dissolve the tartar that has already bonded with the enamel, but it can stop future deposits from forming.
- Fluoride also inhibits the metabolism of acid-producing bacteria thereby indirectly help in tartar control in addition to controlling cavities.
Indications:
1. Individuals clinically diagnosed as heavy calculus formers, and those who want to control regular tartar build up.
2. Individuals looking to control extrinsic stain formation on teeth (eg. tea, coffee, tobacco stains, etc)Guidelines:
1. Children under 12 years of age should not use pyrophosphate-containing toothpastes .
2. XTAR should be recommended for minimum 8-12 weeks and after which doctor should evaluate the results and continue further treatmentStorage:
Keep tube capped when not in use. Store below 30°C.
Contraindications:
Known sensitivity to any of the active ingredients or excipients.
Presentation:
100 gm lamitube.
-
Younifloss
Read More Quick ViewFloss with handle for convenient flossing
Presentation :
Multitufted unwaxed floss.
-
Zingisol 15ml
Read More Quick ViewComposition:
Zinc Sulphate I.P. 2% w/v in an aqueous base.
Astringents
Astringents are chemical compounds that precipitate proteins without penetrating the cells. They affect only the superficial layer of mucosa — making the surface mechanically stronger and decreasing the exudation. The word “astringent” is derived from the Latin word adstringere, which means “to bind fast”. Astringents have relatively low cell permeability, and act generally as irritants in moderate concentrations and caustics in high concentrations.
Mode of action:
Astringents cause contraction of tissues by constricting small blood vessels, extracting water from the tissues or by precipitating proteins. Astringents are used in dentistry to cleanse and tighten the gums.
Indications:
Dentists can apply astringents to gingival tissues
1. to stop bleeding gums
2. Before taking impressions
3. Before doing Class V or root surface restorations.Directions for use:
Take 3 to 4 drops Zingisol on the fingertip and massage each quadrant 3 to 4 times a day, or as directed by the dentist or physician.
Storage:
Store in a cool, dark place. Caution: For external use only.
Presentation:
Plastic bottle of 15ml (0.5 fl.oz) with inbuilt dropper.
Quick Links
Our Products
Information
Contact us
- 216-219, Adarsh Industrial Estate, Sahar Road, Chakala, Andheri (East), Mumbai - 400099
- Fax : 28216928
- +91 22 40065305 / 40065306 / 40065307
- info@icpahealth.com

Selected Icpa Products
Click on Add to cart to add this item in cart.
| PRODUCTS | QTY | PRICE | VALUE in INR |
|---|
Selected Icpa Products
Click on Add to cart to add this item in cart.
| PRODUCTS | QTY | PRICE | VALUE in INR |
|---|